
Fatty liver disease, especially NAFLD, has become a prevalent health concern across the globe, and the burden keeps growing. It occurs when the liver develops inflammation and possibly damage, due to a buildup of too much fat in it. Vitamin B12 deficiency has emerged in recent years as one of the major factors that may be of importance for its development and progression.Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient necessary for numerous metabolic activities that keep our bodies running smoothly, including fat metabolism, thereby making any shortage far-reaching in its consequences on liver health.
How vitamin B12 affects the liver
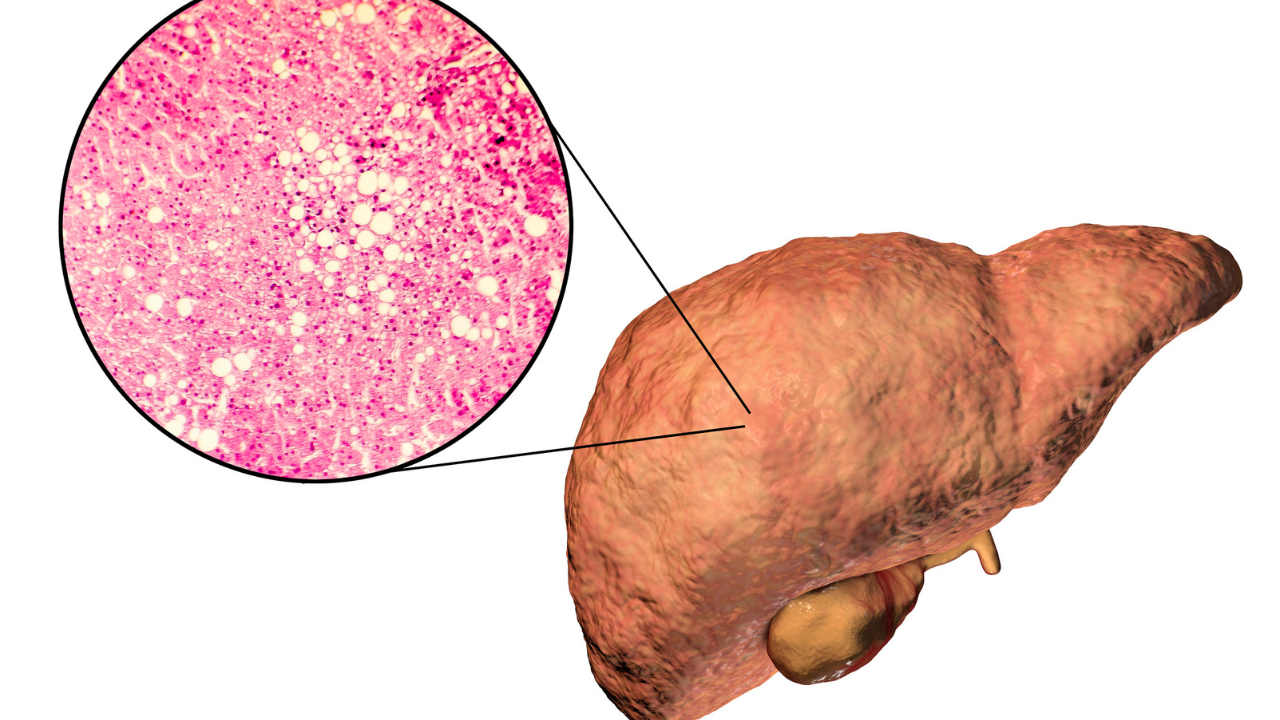
Vitamin B12 is highly essential in the body’s metabolic processes, such as fat breakdown and liver health maintenance. The liver cannot handle fat processing and its exportation when the levels of B12 are low; hence, it deposits that fat within liver cells. The deposition promotes inflammation that can cause scarring and dysfunction of the liver if left unmanaged. Several studies have reported that levels of vitamin B12 are usually low in NAFLD patients compared to individuals with normal health.A deficiency in vitamin B12 has a significant impact on homocysteine levels, which is an amino acid that is linked to increased oxidative stress as well as potential liver damage. This situation can further exacerbate existing liver health issues. However, studies indicate that supplementation with vitamin B12 can effectively lower homocysteine levels and may also lead to an improvement in liver enzyme function. This improvement has the potential to slow down the progression of liver disease. Maintaining adequate B12 levels supports overall metabolic balance, which is crucial for long-term liver health.

Fatigue, weakness, numbness, and poor concentration are common manifestations of Vitamin B12 deficiency. But the signs of liver damage usually remain unnoticed until the disease has reached an advanced stage. The symptoms of fatty liver caused by low B12 can be so well-masked that many will not even guess at their risk. Sometimes this nutrient deficiency is associated with other problems of the liver, such as gallstones. That this is occurring speaks to the active role vitamin B12 plays in the generation of bile and liver metabolism. Early detection and correction of B12 deficiency are important in avoiding serious complications related to the liver.
Prevention and treatment options

Vitamin B12 deficiency may be prevented if the diet contains adequate intake of animal-based foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Vitamin B12 absorption might be problematic for some individuals because of age, use of certain drugs, and digestive system diseases. In such cases, supplements and injections upon recommendation by health professionals will successfully return healthy levels of the vitamin. Regular screenings are able to spot deficiencies early, especially among those at risk for liver disease. Treatment not only corrects the deficiency but may also reduce liver fat accumulation and inflammation, thus easing symptoms and preventing complications.Research on vitamin B12 and fatty liver disease is ongoing and changing. Some trials have shown promising benefits of supplementation with vitamin B12 on liver enzymes and metabolic markers, while others have called for larger studies to firmly establish these effects. The association between B12, homocysteine, and liver health becomes relevant because it explains exactly how vitamin deficiency leads to oxidative stress and eventual tissue damage. Future studies will likely focus on optimizing B12 dosing and combination therapies with other vitamins, including folate, to maximize liver protection. These are hopeful signs toward novel strategies in the management of NAFLD and its related disorders. Vitamin B12 deficiency is a silent yet very serious cause of fatty liver and possibly gallstones.According to International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, NAFLD is a very common health problem in developed countries. Research is now focusing on the role of vitamins especially B12 in the fat buildup in the liver. Vitamin B12 is important for many cell processes including DNA synthesis and fat metabolism.The study published here compared 150 people with NAFLD to 50 healthy controls, excluding those with liver or serious diseases. They found that vitamin B12 levels were significantly lower in NAFLD patients compared to other healthy people. Vitamin B12 deficiency is common in India, and the study noted more males with NAFLD than females.Early detection and replacement may slow down or even reverse some aspects of the liver damage in NAFLD. With more research, vitamin B12 could then form the backbone of policies in the prevention and management of liver diseases and give hope to millions worldwide. Medical consultation regarding testing and treatment options should be done for those with symptoms of deficiency or who have the potential to develop fatty liver for long-term liver health.





